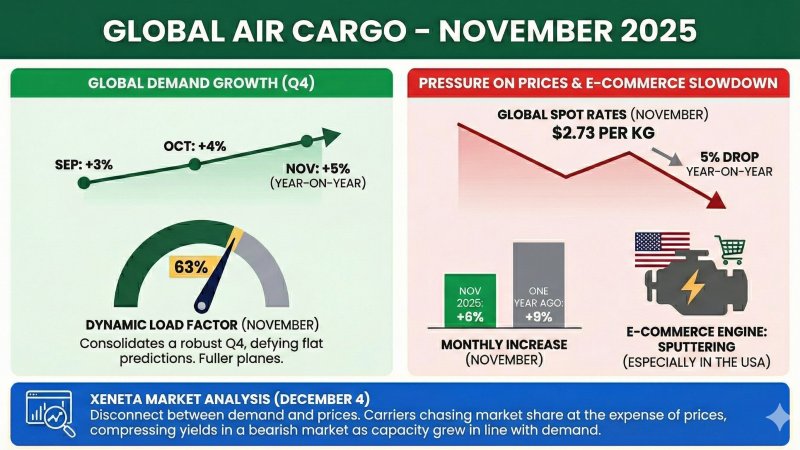
Container shipping heading towards overcapacity
According to the analysis published in issue 734 of Sea-Intelligence Sunday Spotlight, the global container shipping industry is heading towards a cyclical phase of overcapacity expected to peak in 2027, at levels comparable to those seen in 2016—a period marked by intense price wars between carriers. The study is based on a model comparing nominal vessel capacity with forecasted container transport demand, adjusted for four operational factors: the structural slowing down of ships, the impact of port congestion, capacity absorption due to the Red Sea crisis, and expectations of increased scrapping of older vessels. The resulting picture shows a shift from a recent capacity deficit to a significant surplus, with a peak anticipated in 2027. The base scenario assumes the Red Sea crisis will be resolved by mid-2026, returning a substantial share of vessels to service. The forecast remains uncertain, however. The model anticipates higher scrapping levels from 2026, potentially affecting 13% of the world fleet aged over twenty years. A prolonged Red Sea crisis, on the other hand, would continue to absorb capacity and limit oversupply. On the demand side, the outlook depends on actual global GDP growth. Factors such as the continuation of the US–China trade war or new vessel orders could exacerbate future overcapacity, impacting freight rates and sector profitability.
Intermodal train Venlo–Oradea
CargoBeamer has launched a new rail connection between Venlo (Netherlands) and Oradea (Romania), expanding its European intermodal transport network. The service operates six times a week with a transit time of 60 hours. Departures take place from Venlo’s Cabooter terminal from Sunday to Friday and from Oradea’s intermodal terminal from Friday to Wednesday. The train accommodates cranable and non-cranable semi-trailers, refrigerated units, tank containers, ADR cargo and standard containers. It is one of the first direct services for semi-trailers between the Netherlands and Romania, offering an estimated 88% reduction in emissions compared with road transport—about 1,800 kilograms of CO2 per trailer. Rail traction is provided by the Romanian company Routier European Transport, which will use most of the available slots, while remaining capacity is open to the market.
New tracks for the Genoa railway hub
Two new tracks have been inaugurated at the Genoa railway hub, part of the four-track upgrade between the Genoa Voltri and Genoa Sampierdarena stations, within the integrated Genoa Node/Third Giovi Pass project. The works were carried out by the general contractor led by the Webuild Group on behalf of Rete Ferroviaria Italiana. The new infrastructure, approximately 8,500 metres long, includes four tracks: two for metropolitan and regional traffic on the existing coastal line between Voltri and Sampierdarena, and two newly built ones for long-distance passenger and freight services. The development will separate traffic flows, improving service regularity within the Genoa hub and across the regional network. The new tracks connect to the Doria–Monte Gazzo and Polcevera tunnels, the latter about three kilometres long and linked to the Giovi Bypass line at the Polcevera junction. The project represents a key step towards the future direct connection with the Third Giovi Pass for both freight and long-distance passenger trains.
First Dutch test of an unmanned vessel
At the Prinses Margriethaven in Maasvlakte 2, the Port of Rotterdam Authority and Demcon Unmanned Systems have successfully completed the Netherlands’ first trial of an unmanned surface vessel authorised to sail in open waters. The exemption for the test was granted by harbour master René de Vries under the inland navigation police regulations (Bpr), which normally require crew presence on board. Since the legislative change introduced in April 2025, specific exemptions have become possible, and this is the first one issued in the country. The autonomous vessel V3000, three metres long and developed by Demcon Unmanned Systems, operated independently in the Prinses Margriethaven under the supervision of a manned Port Authority unit. Designed for bathymetric surveys in ports, rivers and canals, the V3000 integrates safety systems and high-precision sensors that reduce noise and vibration. The experiment forms part of Rotterdam’s fleet renewal programme, which will replace end-of-life vessels over the next twelve years. According to De Vries, autonomous ships could complement traditional units, improving efficiency and operational safety. The Port Authority is evaluating the use of these technologies to increase sustainability and simplify maintenance.
Iveco hydrogen truck for Bosch
Hylane has introduced in Germany the first hydrogen-powered truck equipped with Bosch fuel cells. The vehicle, manufactured by Iveco at its Ulm plant, integrates Bosch’s Fuel Cell Power Module (FCPM) developed in Stuttgart-Feuerbach, marking an entirely “Made in Germany” collaboration. The truck offers a range of up to 800 kilometres and a gross weight of 44 tonnes. It is operated by the logistics company Schäflein on behalf of Bosch, which will use it to transport products between its Nuremberg site and other fixed routes. The vehicle is leased to Schäflein by Hylane, which manages its operations and collects usage data. In addition to reducing emissions, the main goal is to analyse the real-world performance of the fuel cell system. The data gathered will support the development of next-generation hydrogen propulsion systems for heavy-duty transport.
DHL reverse logistics network
DHL Supply Chain has launched the DHL ReTurn Network, a national multi-client reverse logistics solution designed to optimise returns management efficiently and sustainably. The network uses 11 dedicated centres to handle returns for multiple companies, reducing costs and the need for additional infrastructure. According to DHL, businesses can save between 10% and 50% on total returns processing costs. The system integrates advanced technologies, including the ReSku decision engine, which standardises processes and delivers data-driven insights to maximise value recovery from returned goods. In 2024, DHL prevented more than 200 million pounds of returned merchandise from ending up in landfill.
Solar corridor along the A4
Autostrade Alto Adriatico will start the executive phase in 2026 of a 79-hectare photovoltaic park along the A4 motorway between Venice and Trieste. The €7.7 million “green corridor” project will cover junctions, embankments, exposed areas and canopies. The company expects annual economic benefits of €1.5 million, with a payback period of under five years. A feasibility study and mapping of available areas within 300 metres of the motorway were completed in 2024. Around 85% of the surfaces (67.4 hectares) will be allocated to renewable energy communities open to citizens, businesses and local authorities, generating estimated territorial benefits of €1.3 million per year. This section will be coordinated by the national energy services operator. The remaining 15% (11.6 hectares) will supply the motorway infrastructure itself, cutting energy costs by 68% and reducing annual CO2 emissions by 2,500 tonnes. Construction will take 15 months for the internal systems and up to 21 months for those serving the energy communities.